Home > Prototyping
Prototyping
Integrate EIPEKS’ advanced prototyping technology to build a unique product prototype for you.
Home > Prototyping
Prototyping
Integrate EIPEKS’ advanced prototyping technology to build aunique product prototype for you.
Let's Get in Touch!
If you have any needs, please contact us using the form below.

Design Planning
Make detailed product design plan, clarify product function, appearance, size and other requirements, create detailed design drawings and 3D models to ensure that the design documents are accurate.

Material Selection & Preparation
Select and prepare suitable materials, consider their physical properties and processability to ensure that the selected materials meet the requirements of the product and can realize the design concept and meet the needs of verification and testing.

Technology Selection & Research
Conduct relevant technical research to understand its process flow, limitations and best practices, select appropriate prototyping technologies according to product characteristics and manufacturing requirements, such as 3D printing, injection molding, milling, etc., and then prepare and debug the manufacturing equipment required for the selected technology .
Prototyping Process
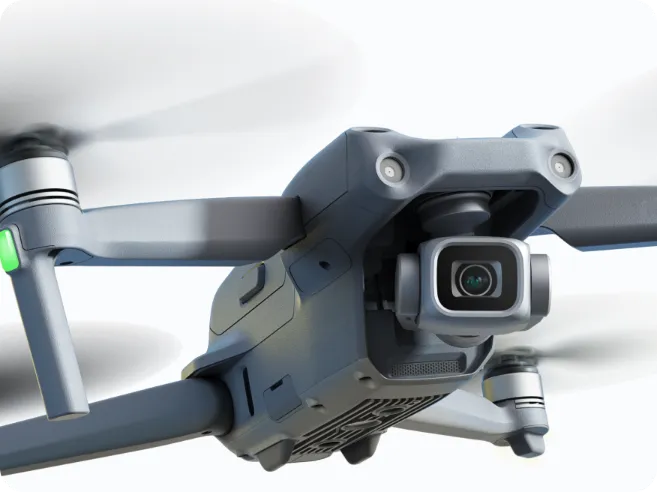



Step 1
Making Prototype
In the field of product development, converting ideas and designs into physical prototypes is a critical and complex process.
File Conversion and Parameter Adjustment
Firstly, convert the design files into a format readable by manufacturing equipment, while adjusting printing parameters, layer thickness, etc.
Initiating Prototyping Processes
Then, start the manufacturing equipment using techniques such as 3D printing, injection molding, or milling to gradually create the physical prototype.
Assembly and Surface Treatment
Finally, assemble the components, ensure proper connections, and perform surface treatments such as polishing, painting, etc., to enhance the visual quality and make the prototype more in line with the design standards.


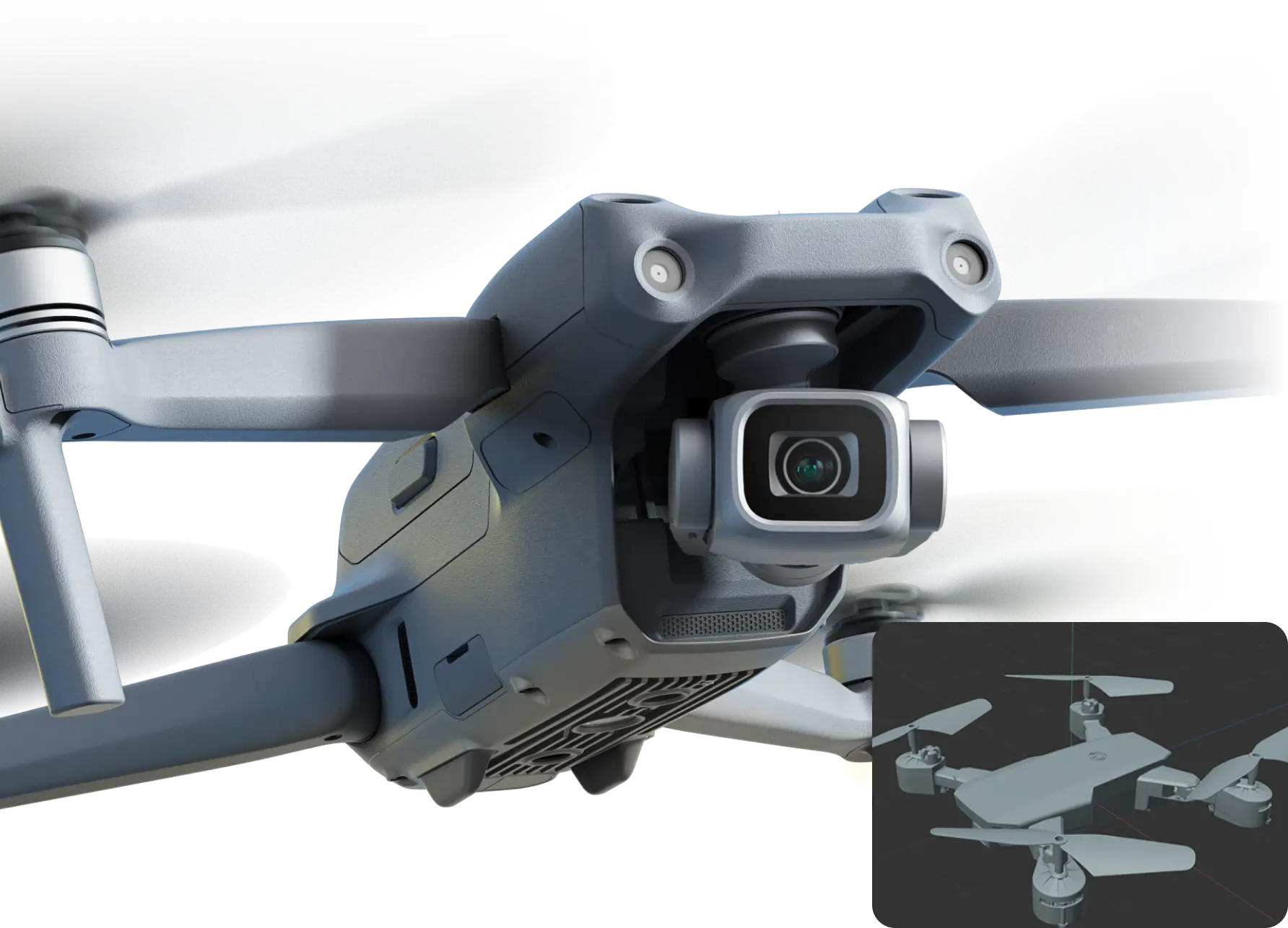
Step 2
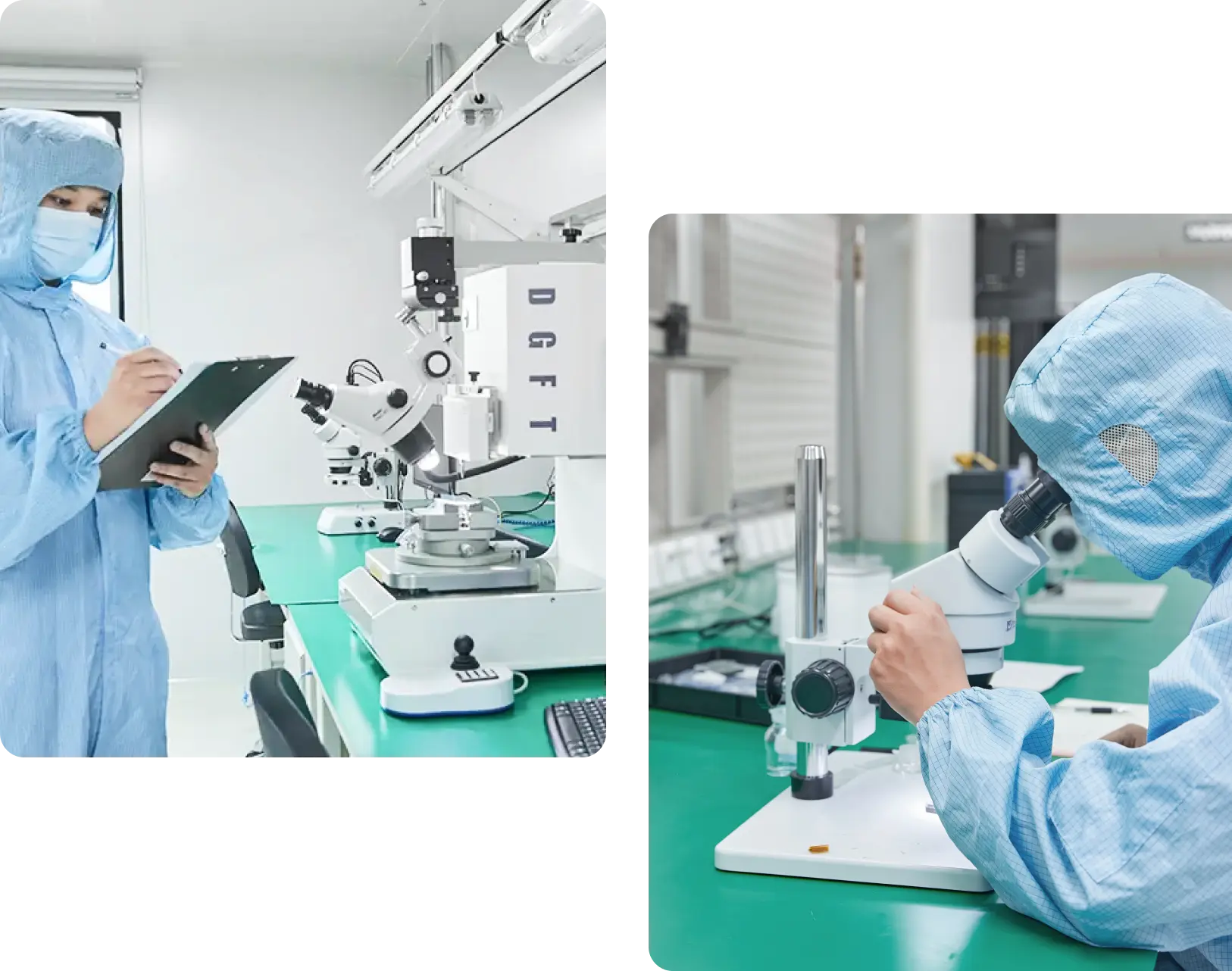
Testing & Optimization
To ensure that the prototype meets the highest standards of quality and performance, it must go through a series of comprehensive and meticulous evaluation and verification steps, and undergo repeated corrections and optimizations.
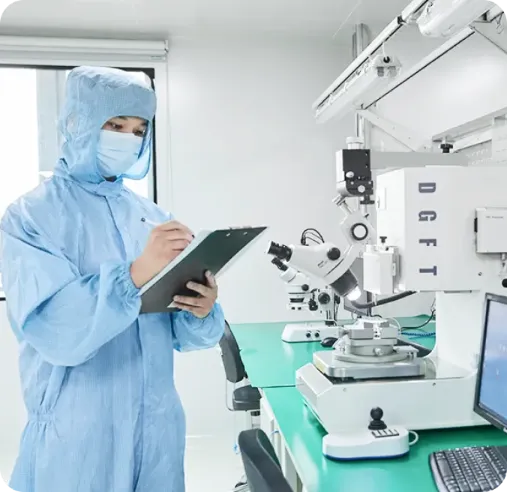
Prototype Quality and Performance Evaluation
Get a full evaluation and verification of the quality and performance of the prototype through dimensional measurement, material quality inspection, appearance inspection, functional and performance testing, durability and environmental testing, and simulated customer experience.
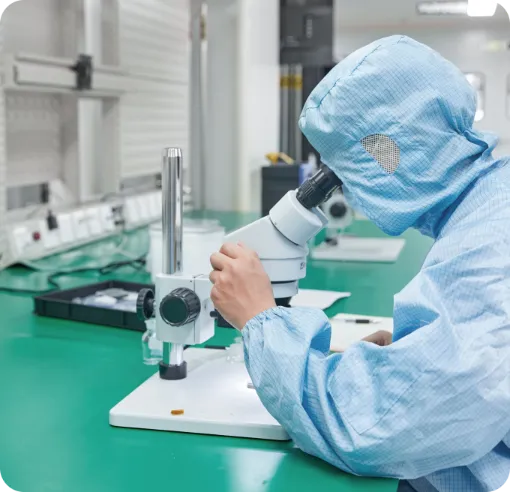
Quantitative Analysis and Iterative Testing
Use statistical analysis methods to obtain quantitative information, and conduct repeated testing and correction when problems are discovered to ensure that the prototype reaches the highest level in terms of size, material quality, appearance, function, performance, durability and user experience, and meets the design requirements, manufacturing standards and user expectations.

Read part cases of our customers.
Product List
EIPEKS has successfully created 1000+ best-selling products. Contact us for more information.

Portable Home Gym
Intelligent Category

Cycling Helmet
Structural Category

Bicycle Electrifcation Kit
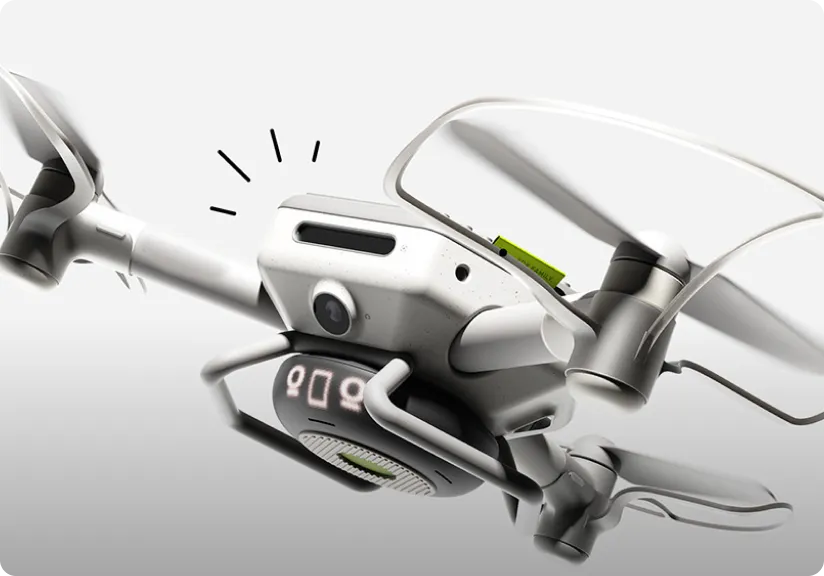
Intelligent Category

Dual-Camera Drone
Intelligent Category

Rehabilitation Glove
Intelligent Category

Quantum Smart Headphone
Intelligent Category
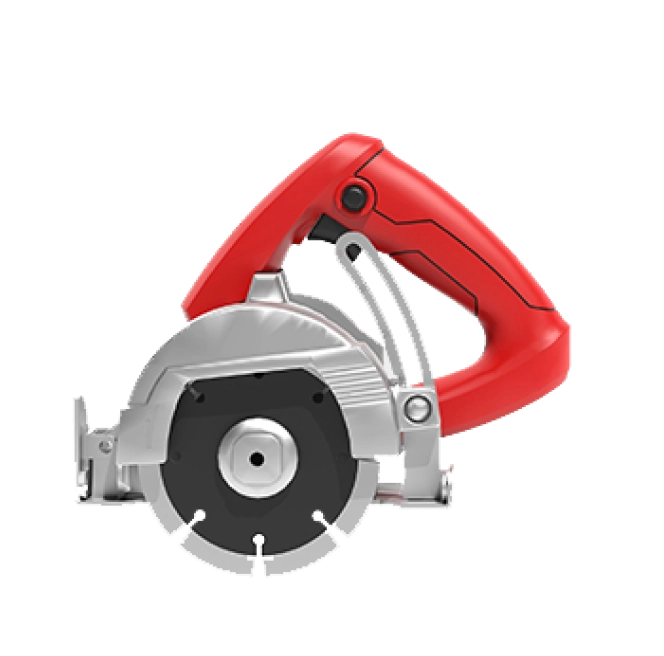
Cutting Machine
Structural Category
Compiles selected product cases from over 1000 successful projects by EIPEKS, with each case disclosed with the client’s authorized consent.
Importance of Prototyping
Verify the Design Concept
Verify the Design Concept
Prototypes are a key tool in transforming theoretical designs into actual physical form. It validates and demonstrates design concepts, helping teams and stakeholders better understand how the product looks, functions, and interacts.
Identify Problems & Improve Design
Identify Problems & Improve Design
By prototyping, the team is able to identify and resolve potential issues before actual manufacturing. Testing prototypes can reveal design flaws, manufacturing challenges, or material selection errors, allowing for early adjustments and optimizations.

User Experience Testing
User Experience Testing
Prototypes make it possible to conduct user experience testing. By simulating actual usage scenarios, the product development team can obtain user feedback and understand users’ feelings and needs for the product in order to make relevant modifications and improvements.

Reduce Development Costs
Reduce Development Costs
By identifying and solving problems at an early stage, prototyping helps reduce the overall cost of product development. It is more economical and reasonable to make adjustments before actual manufacturing than after mass production.
Professional Knowledge

Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
CAD is the core tool in prototyping, and designers need to be skilled in using CAD software to create detailed design drawings and 3D models. CAD skills cover modeling, rendering, animation, etc., ensuring that design documents are accurate, visual, and easy to understand.
Material Engineering Knowledge
Have a deep understanding of the physical properties, mechanical properties, and processing properties of different materials. Choosing appropriate materials is key to ensuring that the prototype meets design requirements. Designers need to consider factors such as material strength, durability, and cost.
Manufacturing Process & Engineering Knowledge
Learn about the various manufacturing technologies involved in the prototyping process, such as 3D printing, injection molding, milling, etc. Designers need to understand the advantages, limitations and best practices of each process in order to consider manufacturing feasibility and efficiency during the design phase.

Human-Computer Interaction Design (HMI)
When prototyping involves user interfaces and user experience, human-computer interaction design becomes critical. Designers need to consider how the product interacts with users to ensure that the product has good usability, ease of use and user satisfaction during use.
We are committed to providing you with full-service support to help your brand succeed.
Whether you are an e-commerce brand, an offline independent brand or an emerging brand, we will tailor a satisfactory product strategy for you.

E-Commerce Brand
We can offer professional technical support covering the entire process from product development and design to smart manufacturing, helping you create competitively distinctive products for online sales.
Competitor research
Multi-channel promotion support
Business needs analysis
Promotional material support
Offline Independent Brand
We can help you create new products based on market needs and help the brand achieve localized design and production.
Market research
User-engaged design
Diversified product lines
Rapid iteration and upgrade
Emerging Brand
We can provide support for innovative design and sustainable production to help you stand out in the market.
Innovative design team
Fast and high-quality delivery
Circular economy design
Supply chain sustainability
FAQ
●
What is the purpose of prototyping?
Prototyping is used to validate product design, test functionality and performance, identify problems in advance, support user experience testing, reduce product development risks, and demonstrate concepts to investors.
●
How long does it take to make a prototype?
Production time depends on product complexity, manufacturing technology selected and the number of tests and modifications required. Typically, prototyping can be completed in as little as 3 days.
●
What materials can be used for prototyping?
Prototyping can use a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, rubber, ceramics, resins, food printing materials, bioprinting materials, etc., depending on the design requirements of the product and the choice of manufacturing technology.
●
How much does prototyping cost?
The cost of prototyping varies based on a variety of factors, including prototype complexity, materials selected, manufacturing technology, quantity, and number of tests required. Typically, prototyping costs are relatively low but can be reasonably estimated early in the project.
●
What aspects does prototype testing include?
Prototype testing involves dimensional measurement, material quality inspection, appearance inspection, functional and performance testing, durability and environmental testing, and simulated customer experience, etc., aiming to fully evaluate the quality and performance of the prototype.



 Anhui
Anhui
Headquarter


Headquarter
D1 Building, Gongtou Liheng Industrial Plaza, Fanhua Avenue, Feixi County, Hefei City, Anhui Province, China
 Shenzhen
Shenzhen
E-Commerce Marketing Research Center


E-Commerce Marketing Research Center
Sanding E-Commerce Building, Bantian Street, Longgang District, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
 Hangzhou
Hangzhou
Product R&D Center


Product R&D Center
A210, Zone A, Dongxi Derbiyi Park, Dongning Road, Shangcheng District, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
 Beijing
Beijing
Hardware and Software Technology and Testing Center

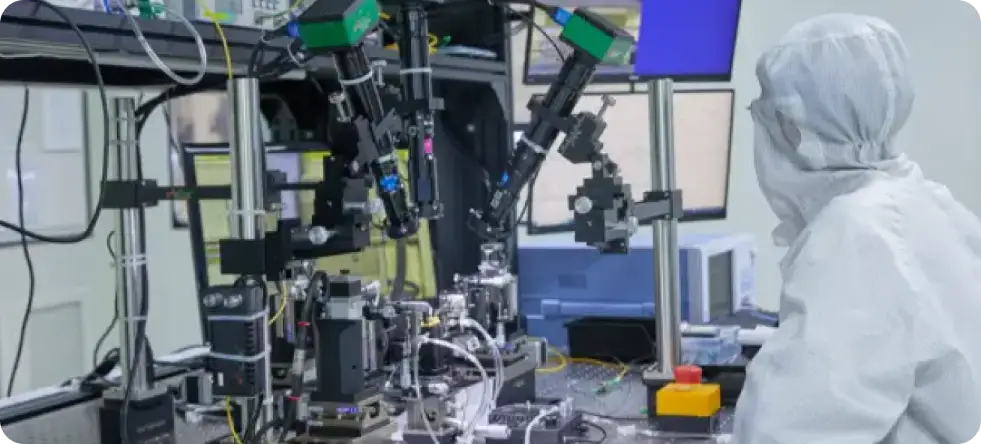
Hardware and Software Technology and Testing Center
No. 536 Huaisha Road, Bohai Town, Huairou District, Beijing, China
 Hongkong
Hongkong
Hong Kong Office


Hong Kong Office
RM 21 UNIT A 11/F TIN WUI IND BLDG NO 3 HING WONG ST TUEN, MUN, NT, HK


